Mature Oral Health: How to Care for Teeth as You Age
Want to keep your teeth strong and healthy long into the future? The best thing you can do is stay on top of your oral health habits today.

A commitment to taking good care of your teeth will pay dividends as you age. Your teeth will remain healthy, and more importantly, they will keep their strength and durability to help you avoid cavities and other unwanted outcomes.
Conversely, a failure to keep up with regular oral hygiene routines can result in a variety of dental health issues that would otherwise be avoidable. If these issues go undiagnosed, they will only get worse with time, making more invasive intervention necessary to resolve them.
A comprehensive oral health care regimen includes elements such as daily rituals, a healthy diet, staying attentive to gum health, and making regular visits to the dentist.
Here is a brief primer for what you should know about maintaining your teeth as you age to keep them healthy and strong long into the future.
Do your teeth change as you get older?
The short answer is yes: your teeth do change as you get older. But how they change is dependent on your health, age, oral care routine, and a range of other factors. In general, though, there are many ways your teeth can change as you age:
- Gums can become thin or recede
- Teeth weaken, becoming more likely to crack or break
- Old fillings or crowns can crack or fall off
- Life-long drug, alcohol, or tobacco use can decay or weaken teeth
- Lifestyle choices and/or genetics can also affect teeth over time
Overall, your daily habits, genetics, and general health can certainly impact your oral health, and this often becomes more apparent with age. The wear and tear can take a toll on your teeth, so it’s important to adopt good habits early on.
When ageing teeth lose their shine
As you age, you may also notice that your teeth begin to lose their white, sparkling shine. This is due in part to the dentin inside the tooth slowing yellowing over time and thickening while the pulp space reduces. This yellow dentin can show through the enamel, especially if the enamel is wearing thin or has cracks.
Further, your teeth can lose their sheen due to your diet. Coffee, tea, tobacco, and red wine are all known to stain teeth and affect their colour.
When do teeth start ageing?
Teeth essentially start “ageing” as soon as they are formed, as your environment, diet, and more can impact your teeth even from a young age. At around 6 years old is when children begin losing their baby teeth and their adult teeth start to emerge. With your adult teeth, the speed of ageing has to do primarily with health, genetics, and environmental factors.
Can ageing teeth be whitened?
Whitening products and treatments are available for people of any age. Anti-stain solutions are popular and powerful ways to keep teeth looking bright and white over time. For deeper and more persistent stains, you may want to visit your hygienist or dentist to form a plan.
How to strengthen your teeth as you age
It’s never too early to start thinking about your oral care routine. Mature oral care refers to oral care for those later in years. This type of care considers the natural wear and tear that occurs on ageing teeth, health, diet, and other factors which may impact the appearance and strength of your teeth
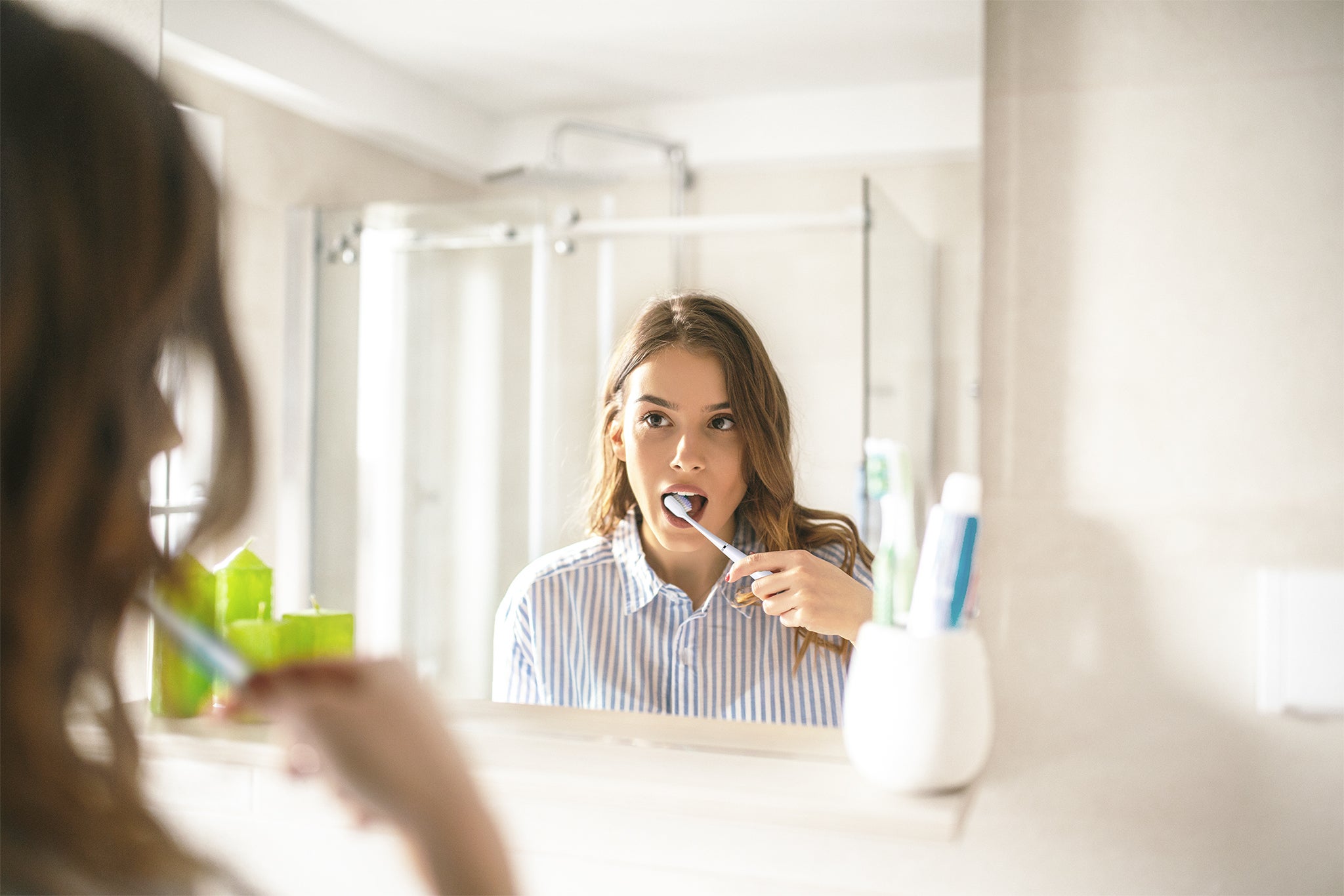
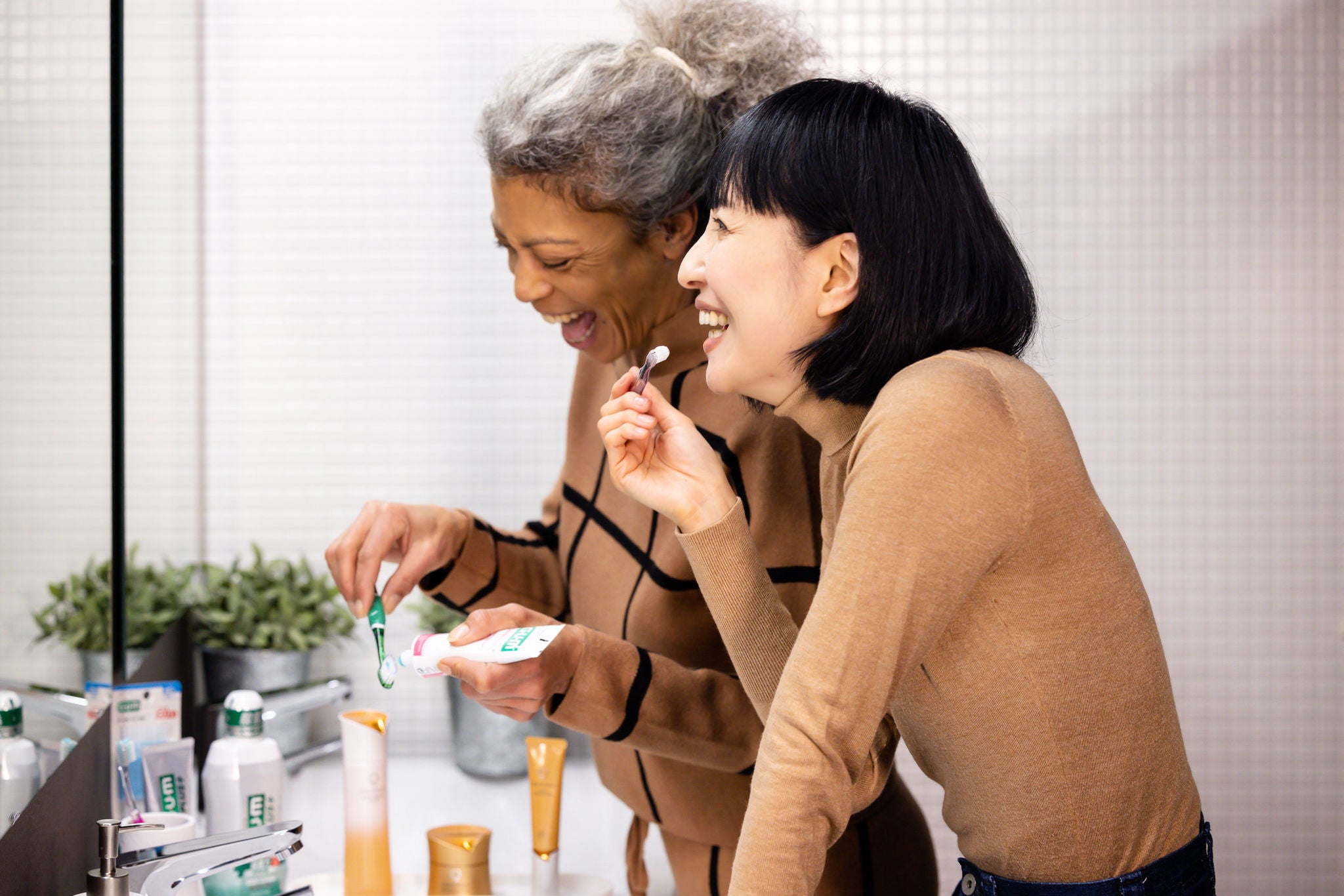
1. Stick to a comprehensive daily oral care ritual
You should brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste to keep them clean and prevent plaque buildup.
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that grows on top of the teeth and can lead to tooth decay and gum disease if not removed. Brushing teeth removes plaque buildup. Try to spend at least 2 minutes brushing every surface of your teeth to remove plaque. Do this once at night before you go to bed, and once in the morning.
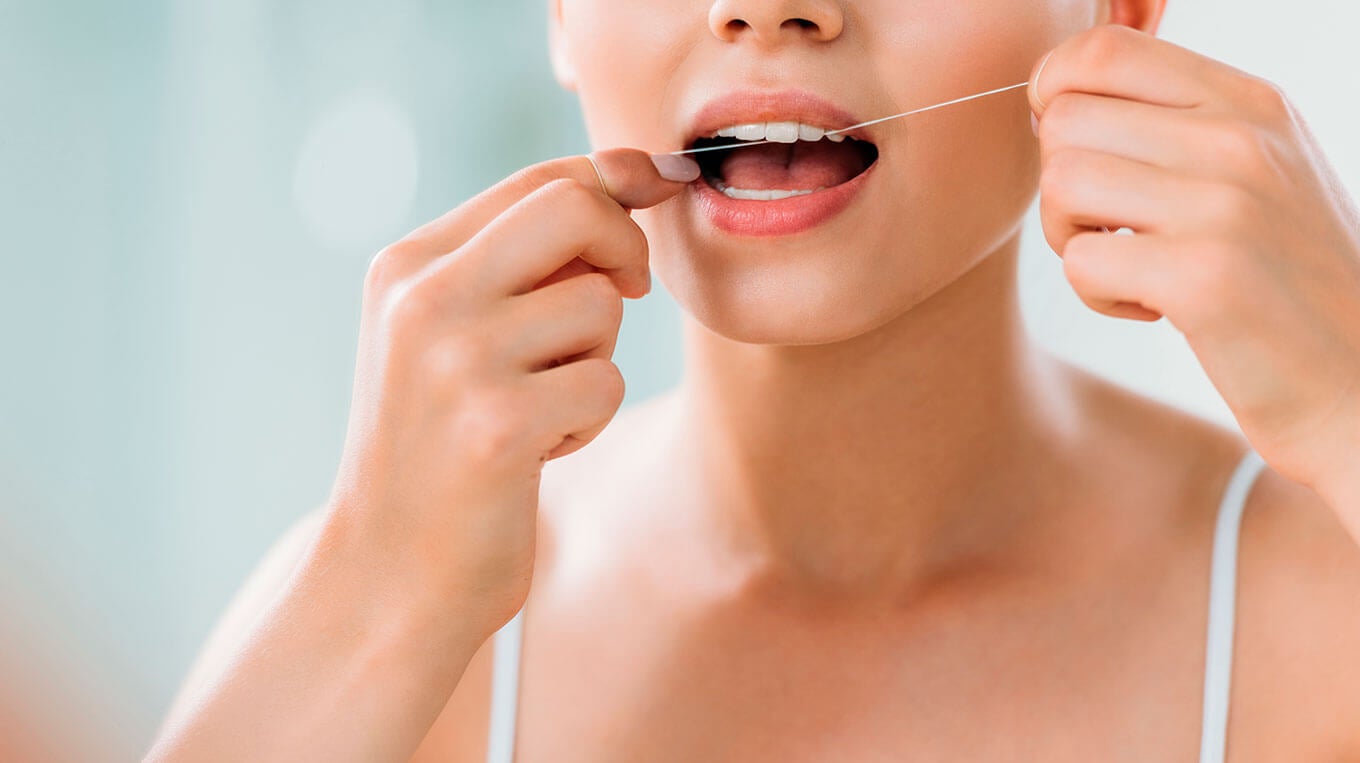
It’s also advisable to clean interdentally once daily to remove food, debris and plaque that gets lodged between your teeth and cannot be removed by toothbrushing only. This is critical for ensuring plaque can’t build in small spaces and turn into tartar.
Both brushing and interdental cleaning help to prevent significant buildup of tartar, the hard deposits that line the teeth and gums. Tartar forms when plaque stays on the teeth and hardens. Tartar is much more difficult to remove than plaque as it can only be removed by the dentist during a cleaning, so preventing its buildup is crucial to maintaining good oral health.

2. Maintain a diet conducive to good oral health
A well-balanced diet is beneficial to your entire body, including your teeth and gums.
Maintain a diet that includes a heavy dose of fruits and vegetables, protein and starchy foods, such as potatoes, bread, rice, and pasta. For the latter, make sure you pick the wholegrain variants for a healthy amount of fiber.
Consume foods and beverages that are high in fat or sugar in small quantities.
Sugar is particularly detrimental to oral health when consumed in excess. So-called “free sugars,” or refined sugars, are the ones that ought to be limited the most. These include any sugars added to food or drinks (think chocolate, candy, sodas, yogurts, breakfast cereals) or sugars found in fruit juices, smoothies, syrups and honey.
Sugars that naturally occur in milk, vegetables and fruit do not count as “free sugars” but will be included in a total sugar count on nutritional labels.
While they are breaking down sugar, bacteria in your mouth release certain acids that can dissolve tooth enamel. The more sugar in your diet, the greater your risk for tooth decay. Regular brushing and interdental cleaning help avoid these effects, but high-sugar diets increase the risk to your oral health, as well as to your overall health through weight gain and potential diabetes risk.
Reducing sugar intake and maintaining a healthy, balanced diet is one of the best ways to keep teeth strong and healthy.
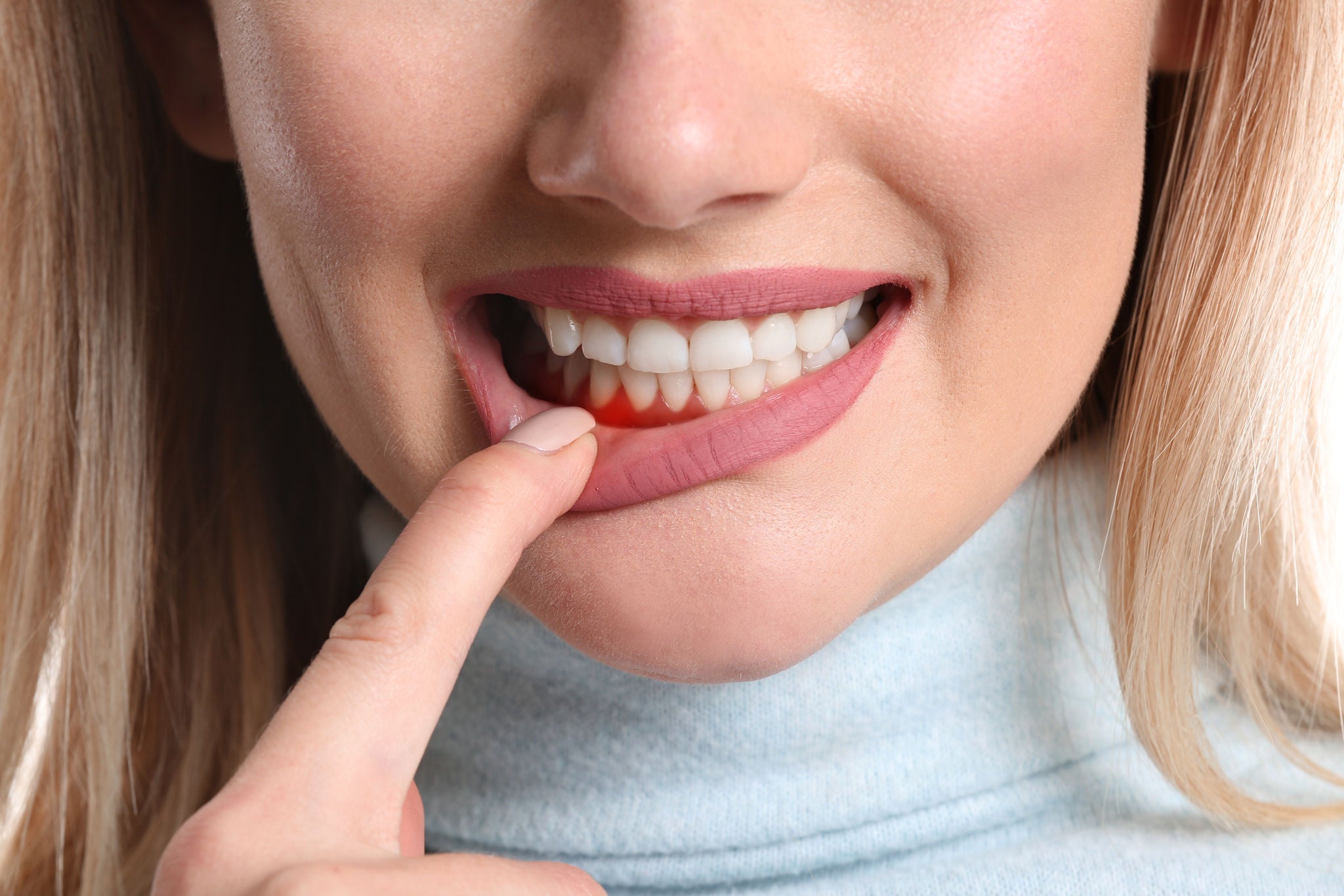
3. Pay attention to gum health
Much of the focus in oral health care is on the teeth, but your gums play a critical role in the long-term picture.
Brushing your teeth helps keep plaque away from the gum lines. Interdental cleaning removes plaque buildup in between the teeth and gets it away from the gums while also strengthening the gums in the process.
When plaque builds up along and under the gum line, it can then cause gum inflammation resulting in bleeding and other problems. Over time, affected gums may begin to pull back, which can cause issues with tooth, stability, and sensitivity.
A focus on gum health can also help you reduce bad breath, which is frequently a result of plaque buildup along and under the gum line.
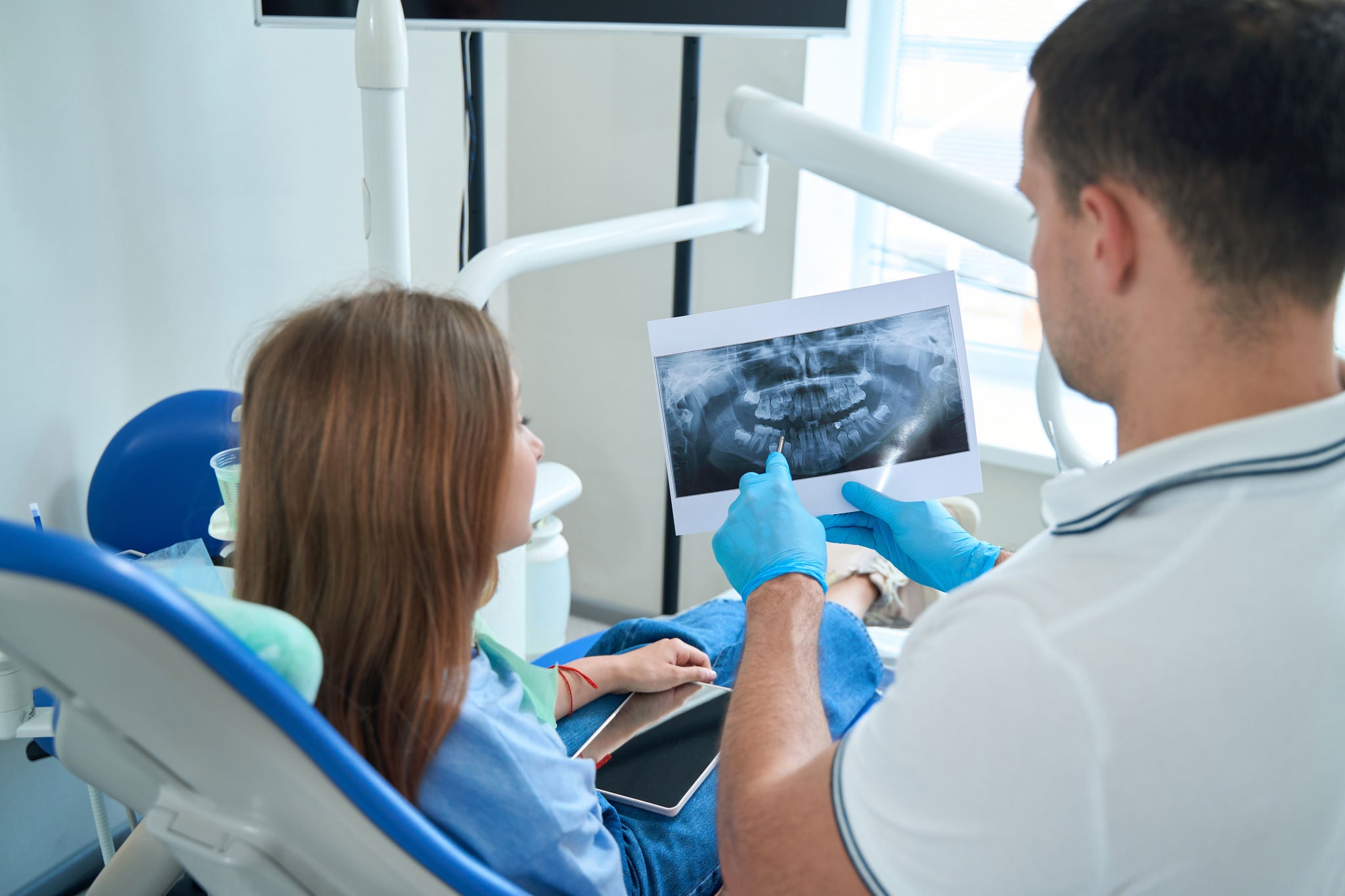
4. Visit your dentist regularly
Aim to visit your dentist and/or dental hygienist twice a year for checkups. Your appointment will often include plaque and tartar removal, teeth cleaning and polishing, and various examinations to determine the health of your teeth.
Visits to the dentist also allow you the opportunity to bring up any concerns you have regarding your oral health. Be sure to listen to and follow the advice given by your dentist.
Even if your concerns seem minor, it’s important to address them early on before they turn into more significant dental problems.
The overarching goal of preventing tooth loss
All of the measures above are important not only for strengthening your teeth and gums, but doing so in pursuit of the ultimate goal: keeping your original teeth as you age. A lifetime of good habits will vastly improve the chances of saving teeth and maintaining their natural function in your later years. And this is important, because nothing beats your own teeth when it comes to eating, speaking, and everything else you need your mouth for. So keeping your teeth is a goal worthy of your dedication.
SUNSTAR GUM® is here to help you learn how to strengthen your teeth and take the best possible care of your mouth at each stage of life. Taking the right steps today and using the right products will greatly improve your oral health down the road.