Gum Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Periodontal Conditions
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health and well-being. Healthy gums support your teeth, which is why neglecting gum health can lead to serious problems, including tooth loss and systemic health conditions like heart disease and diabetes. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn about the importance of gum health, common gum-related issues, and effective strategies to keep your gums healthy and strong.

Gum Diseases: an overview
What is gum disease?
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, refers to inflammation in the structures around the teeth, including the gums, ligaments, and bones. The term 'periodontal' comes from the Greek words peri which means "around" and odont which means "tooth" – so it literally means 'around the teeth.'
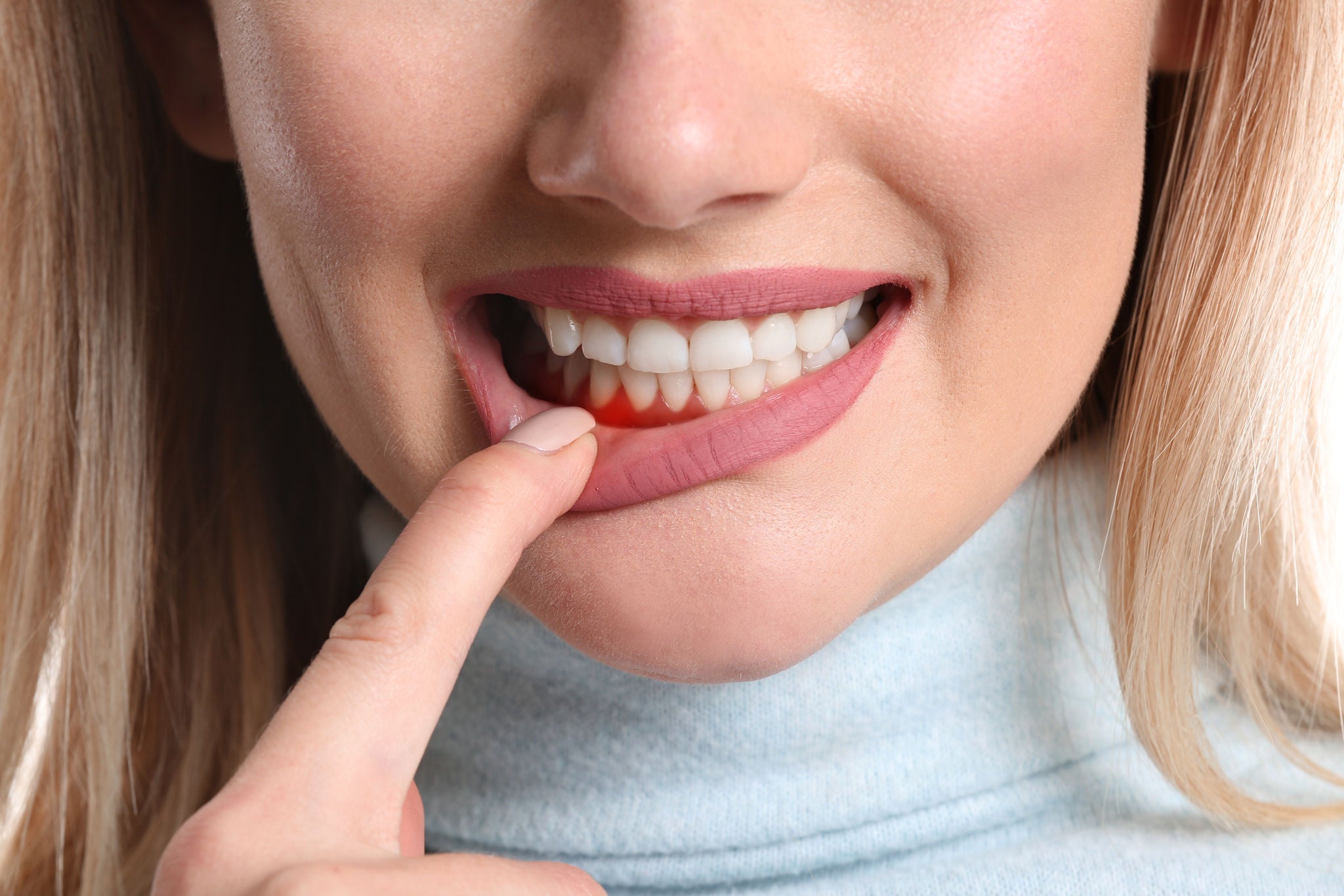
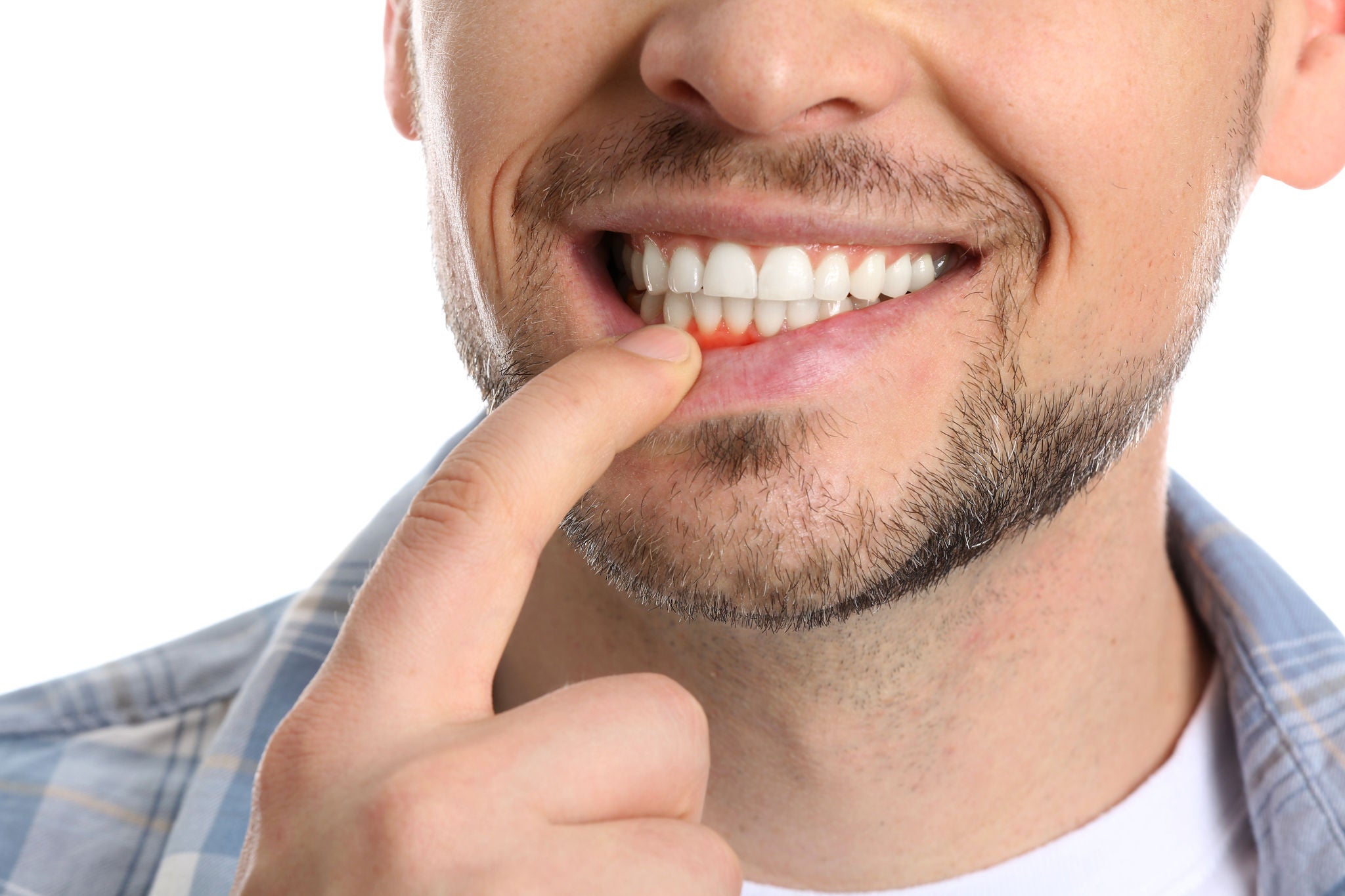
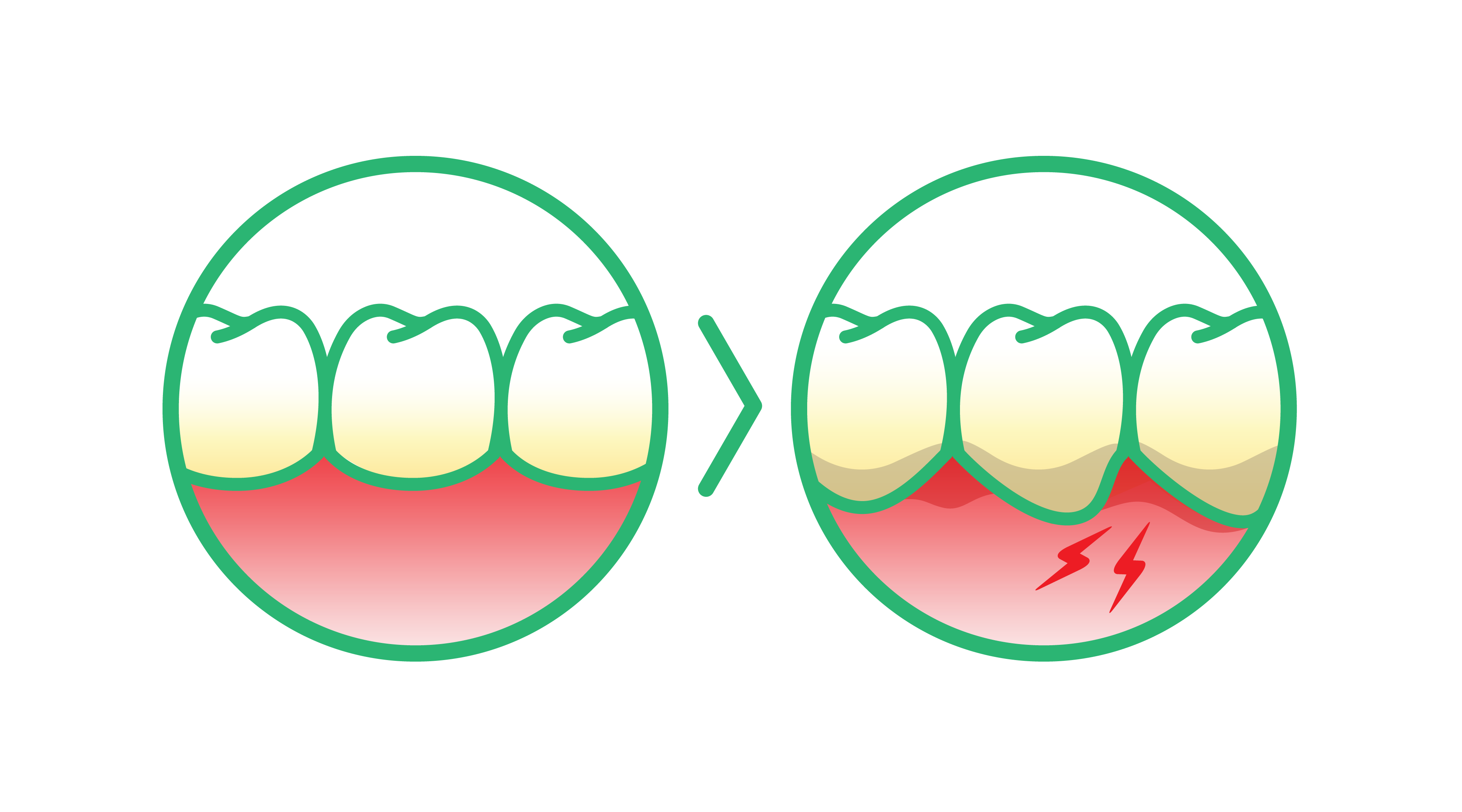
There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage, characterised by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily.
If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and more seriously affect overall health.
Gum disease causes and risk factors
Gum diseases are primarily caused by the build-up of plaque – a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. While poor oral hygiene is a significant cause of gum disease, your oral health can be influenced by various factors beyond improper brushing or lacklustre interdental cleaning. For example, some people are genetically predisposed, but lifestyle also plays an important role.
An unhealthy diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and the body’s ability to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums. Smoking is a significant risk factor, as it impairs blood flow to the gums, hinders healing, and increases plaque accumulation. Stress can also contribute to gum disease by affecting the immune response and leading to neglect of oral care routines.
Orthodontic treatments, while beneficial for aligning teeth, can create challenges in maintaining oral hygiene, making it easier for plaque to accumulate.
Other health issues such as diabetes and cancer can compromise the immune system and exacerbate gum problems, as these conditions often interfere with the body’s natural ability to heal and fend off infections.
Understanding these contributing factors is important for comprehensive gum diseases prevention and management.
Preventing sore gums, gingivitis, and gum disease
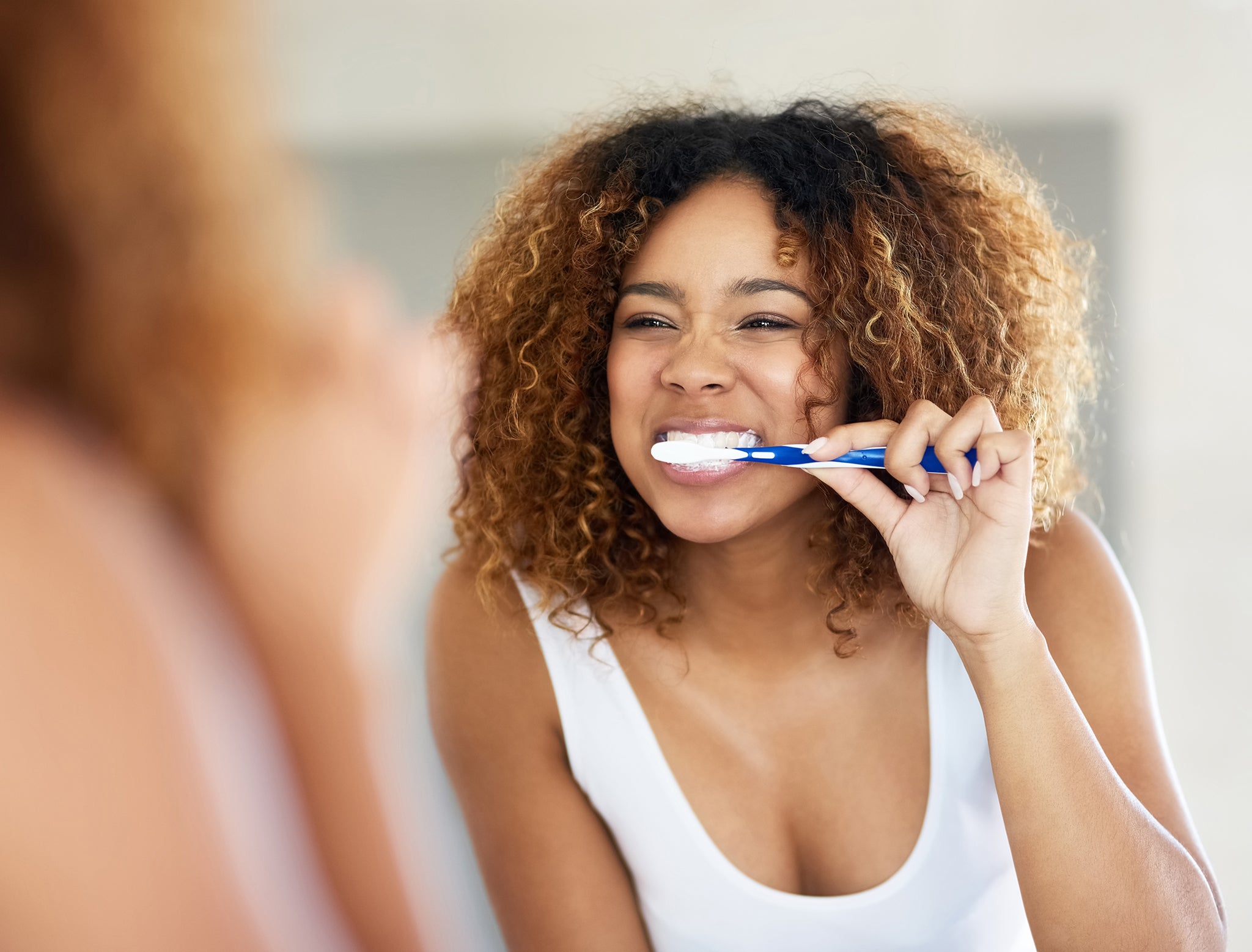
Maintaining a daily oral care routine is essential for preventing gum diseases This includes brushing at least twice a day, daily interdental cleaning, and using mouthwash to reduce plaque build-up. Regular professional dental care is also key for early detection and treatment of gum issues.
Gum Diseases: symptoms and detection
Early signs of gum disease
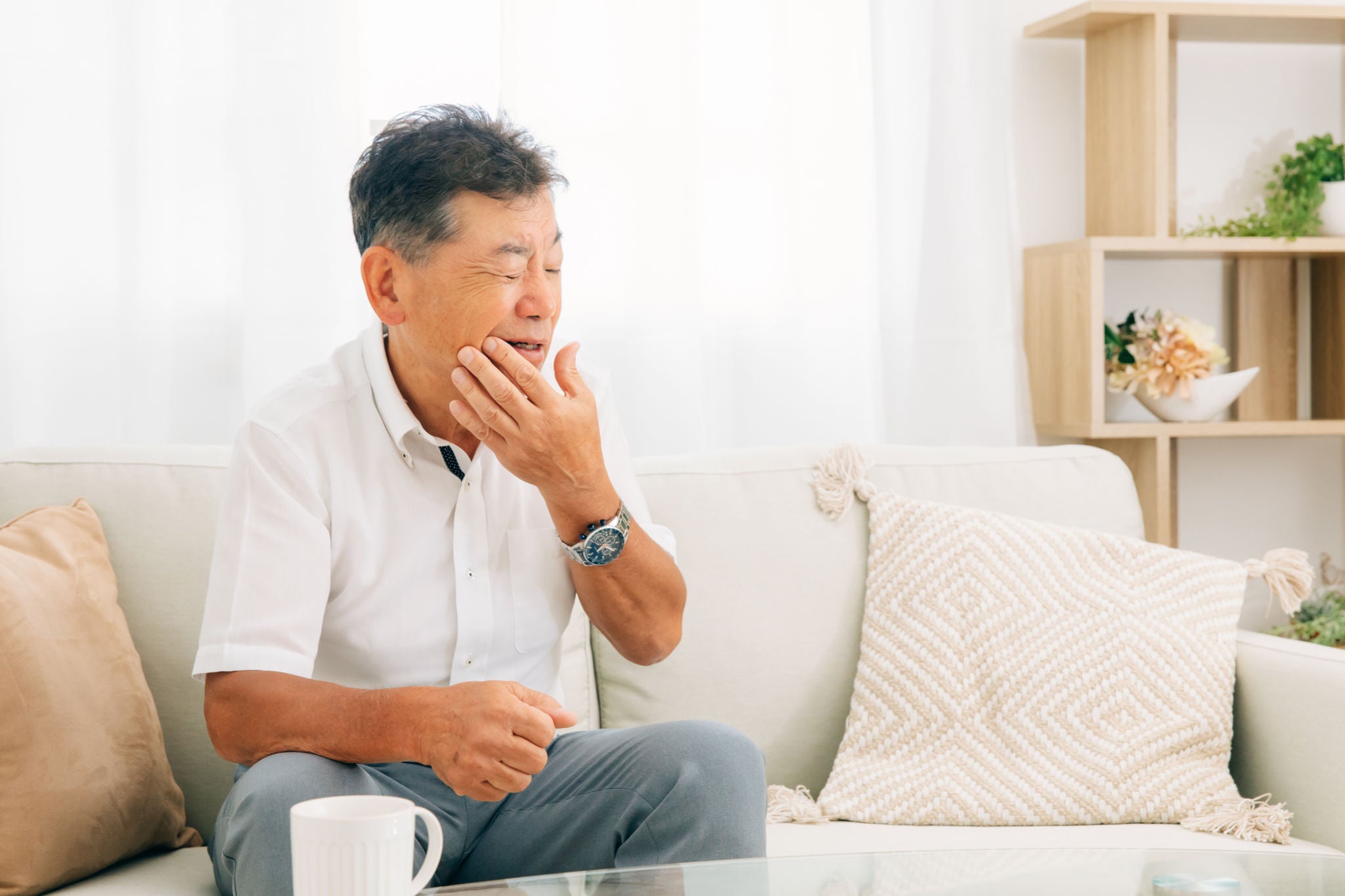
Recognising the early signs of gum disease is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of more severe issues.
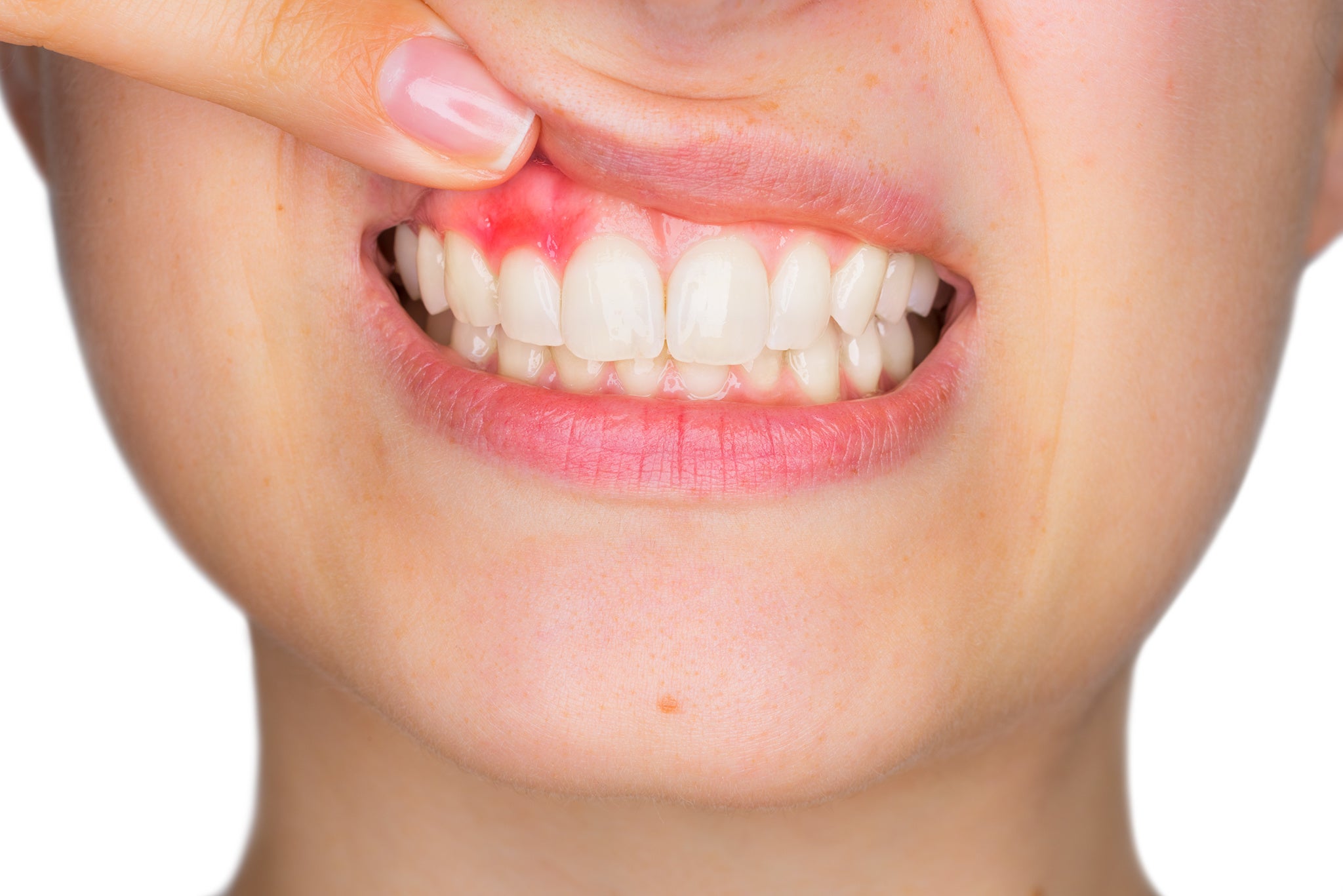
Common symptoms to watch for include red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or interdental cleaning (flossing or using interdental picks or brushes), persistent bad breath, and gums that appear to be pulling away from the teeth.
Early detection is vital as it allows for easier and more effective treatment, and prevents the progression to more advanced stages of gum disease.
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, characterised by inflammation of the gums. Unlike more advanced gum disease, gingivitis can typically be reversed with proper oral care and a visit to your dental professional for regular treatment. Maintaining diligent oral hygiene practices can lead to significant improvements in a matter of days to weeks. As the gums heal, you’ll notice reduced inflammation, less bleeding, and overall better gum health.
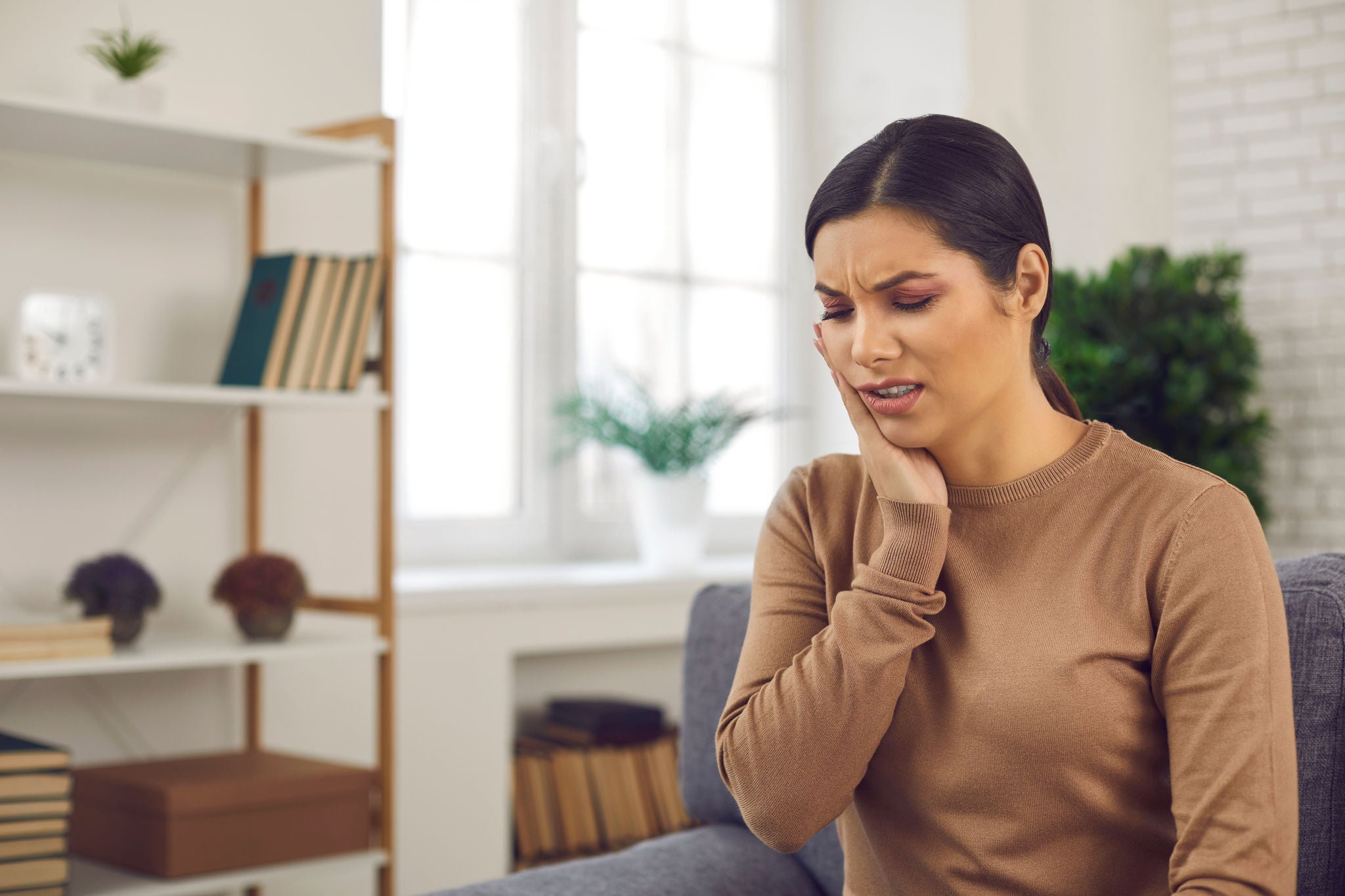
The risk of receding gums
Receding gums can be one of the consequences of gum disease. They pose a significant risk to your oral health, as they can lead to exposed roots, increased tooth sensitivity, and a higher likelihood of decay and tooth loss. Early detection is crucial to managing this condition. If left untreated, receding gums can progress, causing irreversible damage to the supporting structures of your teeth
Gum Diseases: treatment and management
Addressing gum diseases often requires a combination of professional treatments and diligent home care.
Professional treatment
Professional treatments include procedures such as scaling and root planing, which involve deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
In more advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. In any case, frequent check-ups by an oral care professional are crucial to make sure the disease is treated successfully.
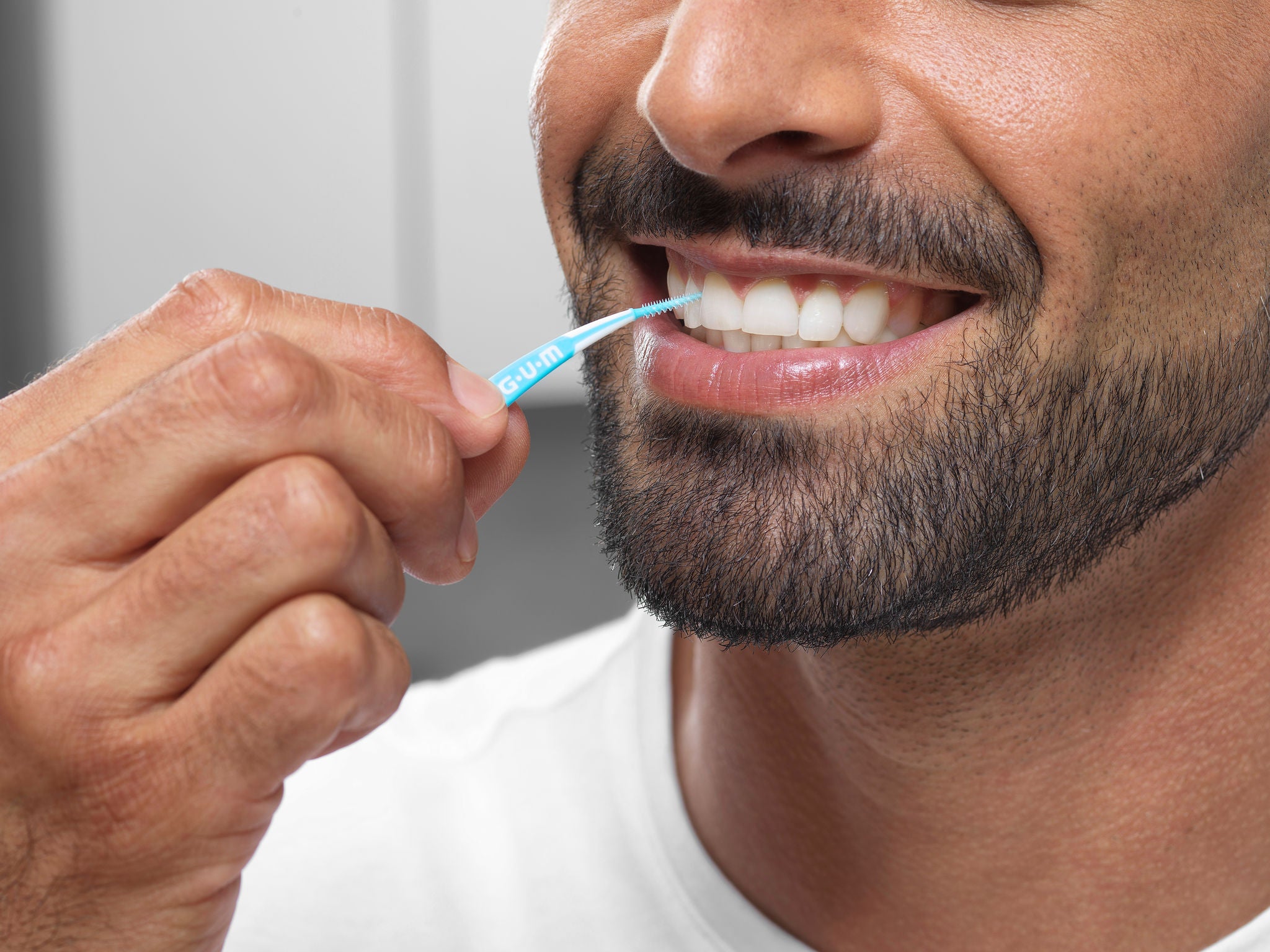
At home, maintaining a rigorous oral hygiene routine is essential. This includes brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and cleaning interdentally each day. In some cases, using antiseptic mouthwash may be required to control plaque.
Home treatment
While recovering from gum disease, using specialised oral care products can help maintain and improve your oral health.
Certain toothpastes and mouthwashes can reduce bacterial growth and plaque build-up, essential for healing gums. Ultra-soft toothbrushes, soft picks and interdental brushes offer gentle yet effective cleaning of all tooth surfaces and along tender gumlines.
We recommend consulting with your dental professional when starting a new intensive at-home oral care routine.
Preventative measures to guard against gum disease
Daily oral hygiene practices
Following a complete daily oral care ritual plays an integral role in preventing gum diseases and promoting overall gum health.
Lifestyle and dietary tips for healthy gums
Adopting a balanced diet and avoiding risky habits can significantly prevent gum diseases. Consuming vitamin C-rich foods like fruits and vegetables helps maintain healthy gums and prevent inflammation, while calcium-rich foods such as dairy products and leafy greens strengthen teeth and bones.
Avoiding tobacco use and limiting sugary and acidic foods can reduce the risk of gum diseases and tooth decay. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and maintain overall oral health.
Start your journey to gum health today
If you put in the time and effort to take good care of your gums, your entire body will thank you. Healthy gums not only support your teeth but also play a significant role in preventing various dental issues and systemic health conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
SUNSTAR GUM offers a range of specialised solutions designed for treating and preventing gum diseases. From advanced toothpastes and mouthwashes to interdental brushes and soft picks, SUNSTAR GUM offers everything you need for comprehensive gum care.
Explore our gum care products to find the right solution for you.